
Occasionally, a sample may be evaluated for the presence of specific antibodies against infectious agents such as Toxoplasma or Ehrlichia.Oyinkan marquis B, Capone PM. If bacteria are identified within a CSF sample, or if large numbers of poorly preserved inflammatory cells are found, then a bacterial culture may be suggested. Electrophoresis will indicate what type of protein is involved in the increase, which will suggest its most likely cause. Further testing can include protein electrophoresis if the CSF protein content is markedly increased (see our handout on protein electrophoresis). Occasionally, neoplastic cells may be found, indicating an underlying tumor within the brain or spinal cord.Ĭan any further evaluation of a CSF sample be undertaken? For example, the presence of bacteria or fungal organisms may be detected along with increased numbers of inflammatory cells, leading to a diagnosis of bacterial or fungal infection. Occasionally a specific diagnosis can be reached. ".evidence to support the most likely diagnosis." The evaluation of CSF frequently does not provide a specific diagnosis, but it will often provide evidence to support the most likely diagnosis when additional factors such as the breed, age, and clinical signs of the animal are taken into account. The cells in the sample are concentrated and placed on microscope slides, which are evaluated by a veterinary pathologist familiar with the normal appearance of CSF cells. The protein content is determined by methods that can detect very low protein concentrations (microprotein techniques). The total nucleated cell and red blood cell counts are done in a specialized counting chamber called a hemocytometer. "A CSF sample must be processed within 30 to 60 minutes of collection or the cells will deteriorate." The veterinary pathologist will evaluate the sample for a total nucleated cell count, a red blood cell count, a total protein determination, and a concentration of the cells in the sample. Therefore, your veterinarian may refer your pet to a facility that is capable of immediately processing the sample. These specific risks are minimized by careful attention to technique and a thorough evaluation of your pet prior to undertaking this procedure.Ī CSF sample must be processed within 30 to 60 minutes of collection or the cells will deteriorate. Other risks are specific to CSF collection, and include the risk of trauma to the spinal cord from the spinal needle, the possibility of brain herniation if the pet has increased pressure in the central nervous system, and the possibility of introducing bacteria through the collection site.
SPINAL FLUID SERIES
Therefore it is important to evaluate the general health of your pet prior to anesthesia by a series of screening tests including a complete blood count, a serum biochemistry profile, and a urinalysis (handouts are available on these subjects). Some risks include those associated with any general anesthetic.
A small amount of CSF (about ½ teaspoon in total) is withdrawn into a sterile collection tube, using a special spinal needle.Īre there any risks associated with CSF collection?
SPINAL FLUID SKIN
The sample site is shaved and the skin is thoroughly cleaned with alcohol or another skin disinfectant. Your veterinarian will choose one of the two collection sites, based upon the clinical signs that your pet is exhibiting. CSF collection requires a general anesthetic. The collection of CSF is usually indicated when the patient shows clinical signs such as seizures, incoordination, circling behavior, neck or back pain, and no obvious cause (such as recent trauma) is known.ĬSF can be collected from two different sites, the cerebellomedullary cistern, located at the back of the head and the lumbar cistern, located at the lower part of the spinal column, near the pelvis. A major function of CSF is to provide a 'cushion' for the brain and spinal cord. "A major function of CSF is to provide a 'cushion' for the brain and spinal cord."ĬSF is found within the brain and in the space that surrounds both the brain and the spinal cord (this space is called the subarachnoid space).
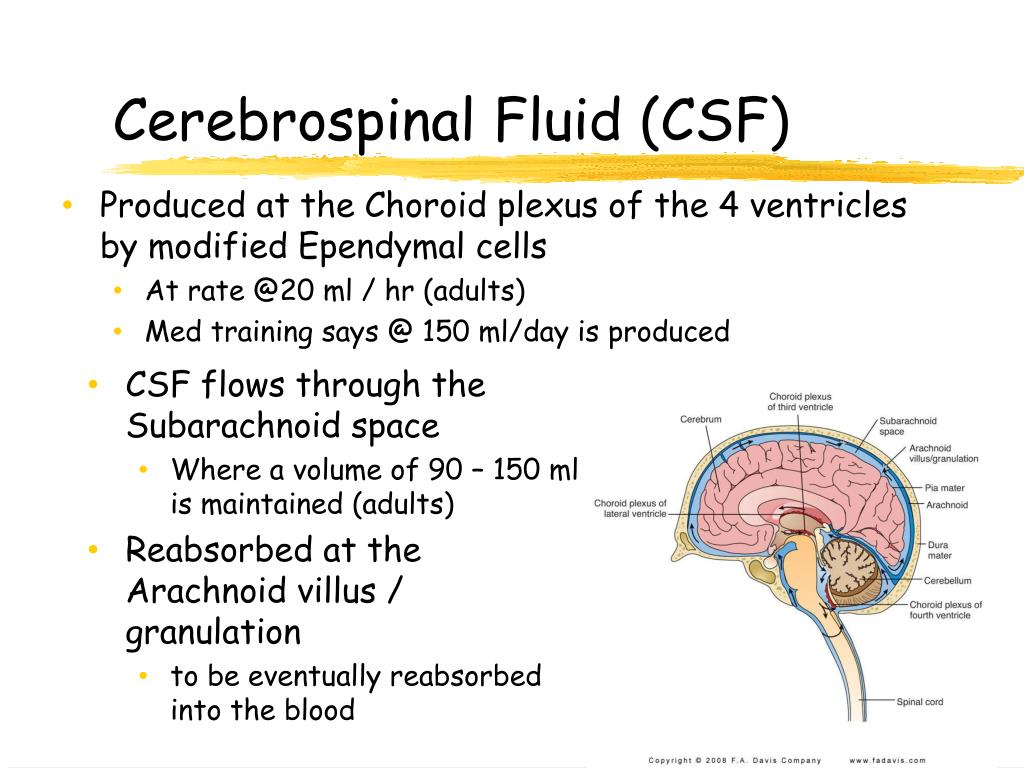
Cerebrospinal fluid (or CSF) is formed within the brain, primarily at specialized sites called the choroid plexuses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
